Digital payments and mobile money have revolutionized the financial landscape, particularly in regions where traditional banking services are limited. Digital payments refer to transactions made through electronic means, encompassing a variety of methods such as online banking, credit/debit cards, and digital wallets.
Mobile money, on the other hand, is a subset of digital payments that involves financial transactions conducted using mobile devices. This method allows users to store, send, and receive money through their mobile phones, bypassing the need for a conventional bank account.
In This Article
The key components of digital payments include electronic funds transfer (EFT), online payment gateways, and digital wallets. These elements work together to facilitate seamless transactions.
Mobile money services, specifically, thrive on the backbone of mobile networks, leveraging SMS, USSD codes, and mobile apps to enable financial activities.
Unlike traditional banking, which often requires physical presence at a bank branch, digital payments and mobile money provide unparalleled convenience and accessibility.
One primary distinction between these modern payment methods and traditional banking lies in their inclusivity. Traditional banking systems often exclude individuals in remote or underserved regions due to the lack of physical infrastructure.
In contrast, mobile money services in Africa have proven transformative, extending financial services to millions who were previously unbanked. This shift is crucial for fostering a cashless economy in Africa, where the reliance on physical cash has historically posed significant challenges.
The rise of digital payments and mobile money in Africa is not just a technological evolution but a social and economic revolution. By providing secure, efficient, and accessible financial services, these innovations are bridging the gap between the formal financial sector and the broader population.
As we delve deeper into this topic, it becomes clear why digital payments and mobile money are becoming increasingly important in Africa, paving the way for a more inclusive and dynamic economic landscape.
Historical Context and Evolution
The journey towards a cashless economy in Africa has been marked by significant milestones and transformative developments. Initially, Africa’s financial landscape was characterized by a high reliance on cash transactions, with limited access to traditional banking services, particularly in rural areas.
The lack of financial inclusion posed a substantial challenge, leaving a large segment of the population without secure and convenient means to manage their finances.
The advent of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa began to reshape this scenario. One of the earliest and most notable milestones was the launch of M-Pesa in Kenya in 2007 by Safaricom, a subsidiary of Vodafone.
M-Pesa’s success served as a catalyst for the proliferation of mobile money services across the continent. It demonstrated the feasibility of leveraging mobile technology to provide financial services to the unbanked population, even in regions with limited banking infrastructure.
Telecommunication companies have played a pivotal role in this evolution. By capitalizing on their extensive network coverage and customer base, they were able to introduce mobile money solutions that bridged the gap between the unbanked and formal financial systems.
The collaboration between telecom operators and financial institutions further accelerated the growth of digital payments in Africa. Banks and fintech companies began to develop and offer diverse digital financial products, enhancing the ecosystem’s robustness and inclusivity.
Key milestones in the evolution of digital payments in Africa include the expansion of mobile money services beyond simple peer-to-peer transfers to encompass bill payments, savings, loans, and international remittances.
Countries like Ghana, Tanzania, and Nigeria have also seen significant adoption of these services, contributing to the continent’s shift towards a cashless economy.
Regulatory frameworks have evolved to support this growth, with governments and central banks implementing policies that encourage innovation while ensuring the security and stability of the financial system.
Overall, the historical context and evolution of digital payments and mobile money in Africa highlight a remarkable transformation. From overcoming initial challenges to achieving key milestones, the continent has made significant strides towards financial inclusion and economic empowerment through the adoption of digital payment solutions.
Factors Driving the Adoption

The rapid adoption of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa can be attributed to several interlinked factors. One of the most significant drivers is the high penetration of mobile phones across the continent.
With over 75% of the population having access to mobile phones, these devices have become a crucial tool for financial transactions, enabling individuals to send and receive money, pay bills, and access various financial services conveniently.
Another critical factor is the pressing need for financial inclusion. A substantial portion of the African population remains unbanked or underbanked, lacking access to traditional banking services.
Digital payments and mobile money services offer a viable solution to bridge this gap, providing millions of people with a means to participate in the financial system. This is particularly important in rural areas, where banking infrastructure is often sparse or non-existent.
The inefficiencies of traditional banking infrastructure further accelerate the shift towards a cashless economy in Africa. Conventional banking methods can be cumbersome, time-consuming, and expensive, often requiring physical presence at bank branches, which may be located far from the customer’s residence.
In contrast, mobile money services offer a faster, more efficient, and cost-effective alternative, enabling users to conduct financial transactions directly from their mobile phones.
Supportive government policies also play a crucial role in fostering the growth of digital payments in Africa. Many African governments have recognized the potential of mobile money services to enhance financial inclusion and drive economic growth.
As a result, they have implemented regulatory frameworks and policies that encourage innovation in the digital payments sector. This includes measures such as licensing mobile money operators, promoting interoperability between different financial service providers, and investing in digital infrastructure.
Collectively, these factors create a conducive environment for the adoption of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa. As mobile technology continues to evolve and more people gain access to digital financial services, the continent is well on its way to achieving a more inclusive, cashless economy.
Key Players and Market Landscape

The digital payments and mobile money ecosystem in Africa is characterized by a diverse range of key players, each contributing to the continent’s shift towards a cashless economy. Leading this transformation are several major companies, including M-Pesa, Orange Money, and MTN Mobile Money, which have established themselves as pivotal in the market landscape.
M-Pesa, operated by Safaricom in Kenya, is arguably the most prominent mobile money service in Africa. Launched in 2007, M-Pesa has grown to become a cornerstone of digital payments in the region, boasting a significant market share. The platform offers various services, including money transfers, bill payments, and loans, making it an essential tool for millions of users. Its success has inspired similar initiatives across the continent.
Orange Money, another major player, operates in multiple African countries, including Côte d’Ivoire, Senegal, and Mali. As a subsidiary of the French telecommunications giant Orange, this service provides a wide range of financial solutions such as money transfers, savings accounts, and microinsurance. Orange Money’s extensive reach and diverse offerings have solidified its position as a leading force in the digital payments sector.
MTN Mobile Money, spearheaded by the South African telecommunications company MTN Group, is also a significant contributor to the cashless economy in Africa. With operations in countries like Uganda, Ghana, and Nigeria, MTN Mobile Money facilitates various financial services, including peer-to-peer transfers, merchant payments, and international remittances. Its expansive network and customer-centric approach have helped it capture a substantial portion of the market.
The competitive dynamics within the digital payments and mobile money space in Africa are intense. Companies continuously innovate to enhance their service offerings and expand their user base.
This competition has resulted in improved financial inclusion, with more individuals gaining access to essential financial services. As these key players continue to evolve, the landscape of digital payments in Africa is poised for further growth and development.
Impact on Financial Inclusion and Economic Growth
The advent of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa has significantly transformed the financial landscape, bringing about profound impacts on financial inclusion and economic growth.
By leveraging digital technologies, these services have provided a platform for marginalized populations to access financial services that were previously out of reach. In rural and underserved areas, where traditional banking infrastructure is often lacking, mobile money services have emerged as a critical tool for bridging the financial inclusion gap.
One of the key benefits of digital payments in Africa is the democratization of financial services. Individuals who were previously excluded from the formal financial system can now perform essential financial transactions such as saving, borrowing, and transferring money.
This increased access to financial services has empowered many to engage in economic activities that contribute to their livelihoods and overall economic growth. For example, small business owners and entrepreneurs can now receive payments seamlessly, manage their finances more effectively, and invest in expanding their operations.
Moreover, the shift towards a cashless economy in Africa has broader economic implications. As more people adopt digital payment systems, there is a reduction in the reliance on cash, which in turn decreases the risks associated with cash handling such as theft and fraud.
This transition also enhances the efficiency of financial transactions, reducing the cost and time involved in processing payments. The ease of digital transactions encourages more economic activities, stimulates consumer spending, and drives economic development.
Furthermore, increased financial inclusion through digital payments and mobile money services has the potential to foster sustainable economic growth. By integrating more people into the financial system, these services help to mobilize savings, increase investments, and facilitate credit access.
This, in turn, supports economic resilience and stability, enabling communities to better withstand economic shocks. The ripple effect of financial inclusion is evident in the improved quality of life, higher levels of education, and overall economic advancement of previously marginalized populations.
Challenges and Barriers to Adoption
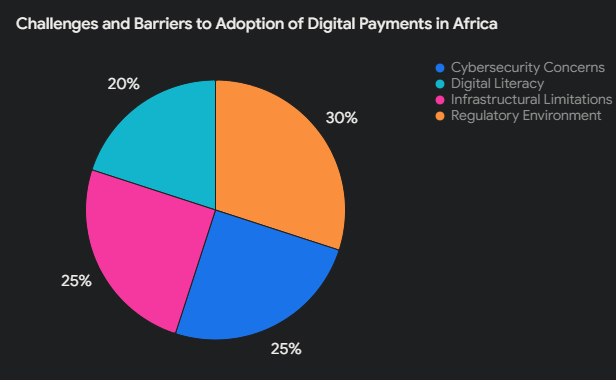
The journey towards a cashless economy in Africa is fraught with numerous challenges and barriers that hinder the widespread adoption of digital payments and mobile money services. One of the primary obstacles is the regulatory environment.
Many African countries have complex and evolving regulatory frameworks that can create uncertainty for both service providers and users. Regulatory inconsistency between different regions within a country can also complicate the scaling of digital payment solutions.
Cybersecurity poses another significant challenge. As digital payments and mobile money services become more prevalent, the risks associated with cyber-attacks and fraud increase.
Many users are wary of adopting these technologies due to concerns about the safety of their financial information. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to build trust and ensure the security of transactions in the digital payments ecosystem.
Digital literacy is another critical barrier. A significant portion of the African population lacks the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively use digital payment platforms.
This is particularly true in rural areas where educational resources are limited. Efforts to enhance digital literacy must be prioritized to facilitate the adoption of mobile money services and foster a cashless economy.
Infrastructural limitations also play a considerable role. The availability of reliable internet and mobile network coverage is essential for the functioning of digital payment systems. However, many regions in Africa still suffer from poor connectivity and limited access to technology. This digital divide exacerbates the challenge of implementing and expanding digital payment solutions across the continent.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving collaboration between governments, private sector stakeholders, and international organizations.
By creating conducive regulatory environments, enhancing cybersecurity, promoting digital literacy, and improving infrastructural development, Africa can overcome these barriers and fully realize the potential of digital payments and mobile money services.
Case Studies: Success Stories and Lessons Learned

In recent years, the landscape of digital payments in Africa has been profoundly transformed. Several African countries have emerged as pioneers, showcasing successful implementations of mobile money services that have significantly contributed to the shift towards a cashless economy. These case studies offer valuable insights into the strategies and factors that have driven their success, providing a blueprint for other regions to follow.
One of the most celebrated success stories is that of Kenya’s M-Pesa. Launched by Safaricom in 2007, M-Pesa revolutionized the way financial transactions are conducted, enabling millions of Kenyans to send and receive money, pay bills, and purchase goods and services using their mobile phones.
The widespread adoption of M-Pesa can be attributed to several key factors: a robust agent network, strong regulatory support, and a deep understanding of the local market’s needs. M-Pesa’s success demonstrates the critical role that a well-developed infrastructure and supportive policies play in fostering the growth of digital payments in Africa.
Another remarkable example is Nigeria’s Paga, a mobile payment platform that has gained significant traction since its inception in 2009. Paga’s success lies in its innovative approach to financial inclusion, targeting both urban and rural populations with user-friendly solutions.
By partnering with banks and other financial institutions, Paga has created a comprehensive ecosystem that facilitates seamless transactions and enhances financial accessibility. The lesson from Paga’s journey is the importance of collaboration and strategic partnerships in scaling mobile money services effectively.
In Ghana, the introduction of MTN Mobile Money has also yielded impressive results. Launched in 2009, MTN Mobile Money has become a major player in the digital payments arena, offering a wide range of services including peer-to-peer transfers, bill payments, and savings accounts.
The platform’s success can be attributed to extensive marketing campaigns, a strong agent network, and continuous innovation to meet evolving customer needs. Ghana’s experience highlights the significance of customer-centric approaches and continuous improvement in maintaining the momentum of digital payment adoption.
These case studies underscore the transformative potential of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa.
By examining the successful strategies employed by Kenya, Nigeria, and Ghana, other regions can glean valuable lessons on the importance of infrastructure, regulatory support, partnerships, and customer focus in driving the shift towards a cashless economy.
As more countries embrace these principles, the future of digital payments in Africa looks promising, paving the way for greater financial inclusion and economic growth.
Future Trends and Opportunities
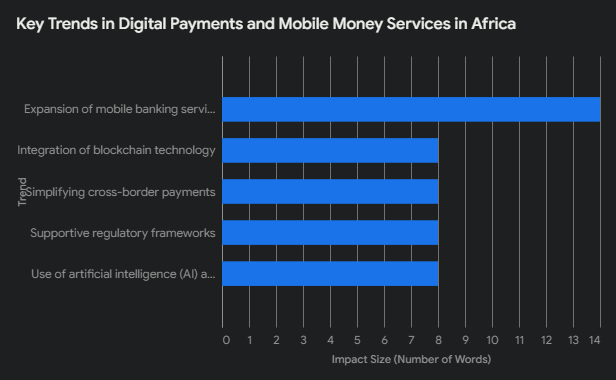
The landscape of digital payments and mobile money services in Africa continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and increasing user adoption. One of the most significant future trends is the integration of blockchain technology.
Blockchain offers enhanced security and transparency, which could revolutionize how transactions are conducted, ensuring greater trust and efficiency in the financial ecosystem. Financial institutions and fintech startups are already exploring blockchain-based solutions to address existing challenges in the sector.
Another promising development is the expansion of mobile banking services. With smartphone penetration on the rise, more Africans are gaining access to mobile banking platforms, facilitating a shift towards a cashless economy.
These platforms are not only providing traditional banking services but also innovative solutions like microloans and insurance, tailored to meet the unique needs of the unbanked and underbanked populations.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning is also poised to transform the digital payments landscape. AI can enhance fraud detection and improve customer service through chatbots and automated systems. Moreover, data analytics powered by AI will enable businesses to gain deeper insights into consumer behavior, helping them to offer more personalized and efficient services.
Cross-border payments remain a significant area of opportunity. Simplifying and reducing the cost of cross-border transactions can facilitate trade and economic growth. Fintech companies are actively working on solutions that leverage digital payments to make cross-border transfers more seamless and affordable, promoting financial inclusion on a broader scale.
Lastly, regulatory frameworks will play a crucial role in shaping the future of digital payments in Africa. Governments and regulatory bodies are increasingly recognizing the importance of fostering innovation while ensuring consumer protection and financial stability.
Collaborative efforts between the public and private sectors will be essential in creating an enabling environment for the growth of digital payments and mobile money services.
As the sector continues to grow, the potential for digital payments and mobile money services to drive economic development and financial inclusion in Africa is immense. Emerging technologies, innovative solutions, and supportive regulatory frameworks will be key to unlocking this potential and paving the way for a more inclusive and cashless economy in Africa.
Digital Payments & Mobile Money in Africa: Your Questions Answered

1. What is mobile money, and how does it work in Africa?
Mobile money allows people to store, send, and receive money using their mobile phones, often without needing a traditional bank account. In Africa, it has become a primary means of financial transaction for many.
2. Why has mobile money become so popular in Africa?
Several factors contribute to its popularity: limited access to traditional banking, widespread mobile phone usage, convenience, affordability, and innovative solutions tailored to local needs.
3. Which African countries are leading in mobile money adoption?
Kenya, Ghana, Tanzania, Uganda, and Zimbabwe are often cited as leaders, but the trend is growing across the continent.
4. What are the main benefits of digital payments and mobile money for individuals and businesses in Africa?
Individuals: Financial inclusion, easier bill payments, secure transactions, access to savings and credit, and reduced reliance on cash.
Businesses: Expanded customer base, streamlined transactions, reduced cash handling risks, and access to new markets.
5. How has mobile money impacted financial inclusion in Africa?
Significantly! Mobile money has given millions of previously unbanked individuals access to financial services, empowering them economically.
Discover more from Ken Arhin
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.










